Guys, Let's Keep It Safe!
The World Health Organization reports that nearly 1 million STIs are acquired each day across the globe [1]. Specifically, India sees an estimated 30 million new STI cases annually [2]. Infections caused by more than 30 different bacteria, viruses, or parasites are recognised to be sexually transmissible via unprotected oral, vaginal, or anal sex. Many STIs in men may not manifest symptoms or only show very mild ones, making it possible for individuals to carry an infection without realizing it. Therefore, regular STD testing is crucial for those who are sexually active. [3].
Bacterial STIs Affecting Men
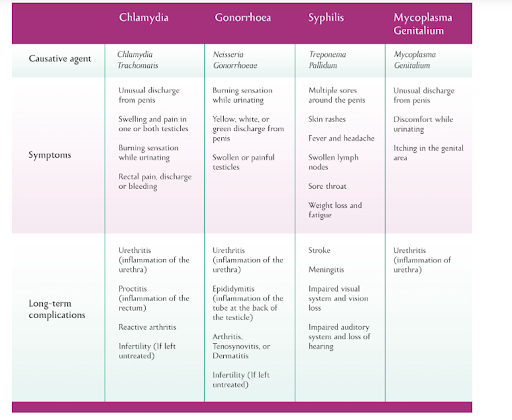
Among the bacterial STDs, Chlamydia, Gonorrhoea, and Syphilis are particularly prevalent worldwide. Fortunately, these diseases can be cured with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment [4]. However, WHO has expressed concerns over the growing resistance of Gonorrhoea-causing bacteria to antibiotics, potentially complicating future treatment efforts [5].
Viral STDs
Viral STDs such as Hepatitis B, Herpes, and HIV present challenges due to their incurable or chronic nature.
- Vaccinations against Hepatitis B are widely available, and research is advancing towards vaccines for genital herpes and HIV [10].
- Herpes is caused by two types of the herpes simplex virus. Type 1 primarily causes oral herpes but can lead to genital herpes through oral-genital contact, while Type 2 is transmitted through sexual contact and causes genital herpes.
- Trichomoniasis, caused by the TrichomonasVaginalis, often goes unnoticed as over 70% of those infected exhibit no symptoms [11]. Symptoms, when present, can include a burning sensation after urination or ejaculation, penile irritation, and unusual discharge. Fortunately, trichomoniasis is curable [12], emphasizing the importance of STD testing for early detection and treatment.
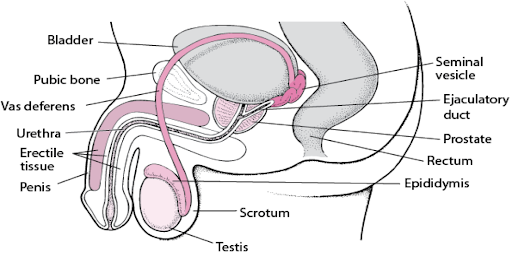
Prostatitis, Epididymitis, and Orchitis
Prostatitis, Epididymitis, and Orchitis, unique to men’s reproductive health, can impact well-being and quality of life. Prostatitis and Epididymitis may result from bacterial STIs, such as chlamydia or gonorrhoea, and can spread through unprotected sexual intercourse. These conditions can also stem from non-infectious causes like trauma or autoimmune reactions. Additionally, viral orchitis, caused by the mumps virus, can be transmitted between individuals, including males, through respiratory droplets [13, 14].
- Prostatitis refers to the inflammation of the prostate gland, which can result from bacterial infections and non-bacterial origins. Symptoms often include discomfort, pain in the pelvic area, difficulties with urination, and sometimes flu-like symptoms in acute cases [15].
- Epididymitis is characterized by inflammation of the epididymis, often due to bacterial infection or sexually transmitted diseases like Chlamydia or Gonorrhoea. Symptoms involve pain and swelling in the testicles, which may be accompanied by fever, chills, and urinary symptoms [16].
- Orchitis, an inflammation of one or both testicles, can be caused by bacterial or viral infections, including mumps. Men with orchitis may experience swelling, tenderness, nausea, and fever. Viral orchitis may resolve on its own, but bacterial orchitis requires antibiotic treatment [17].
CONCLUSION
Awareness and understanding of STIs are critical for maintaining reproductive health and preventing the spread of infections. Regular screening and early treatment can mitigate the severe reproductive consequences of untreated STIs, safeguarding both individual and partner health.
Author

